Importance of Dental Care
Prevalence of Periodontal Disease in Dogs
The prevalence of periodontal disease in dogs is a significant concern among pet owners and veterinary professionals alike. This condition, characterized by inflammation and infection of the tissues surrounding the teeth, affects a substantial proportion of the canine population. According to recent studies, up to 80% of dogs exhibit signs of periodontal disease by the age of three. The severity of the disease varies, with some dogs experiencing mild gingivitis while others suffer from severe periodontitis that can lead to tooth loss and systemic health issues.
The development of periodontal disease in dogs is influenced by several factors, including genetics, breed, diet, and oral hygiene practices. Certain breeds, such as small and toy breeds, are more susceptible due to their crowded teeth and predisposition to dental issues. Additionally, a diet high in sugars and carbohydrates can contribute to the buildup of plaque and tartar, exacerbating the problem.
Regular veterinary check-ups and professional dental cleanings are essential for maintaining good oral health in dogs. However, preventive measures at home are equally important. Brushing teeth with a dog-specific toothpaste, providing dental chews and toys designed to reduce plaque, and offering a balanced diet can significantly decrease the risk of periodontal disease.
Early detection and intervention are crucial for managing periodontal disease in dogs effectively. Owners should be vigilant for signs such as bad breath, swollen or bleeding gums, and loss of appetite. Prompt treatment, including scaling and root planing under general anesthesia, can halt the progression of the disease and preserve the dog's dental health.
In conclusion, understanding the prevalence and causes of periodontal disease in dogs empowers pet owners to take proactive steps towards prevention and early intervention. By incorporating regular dental care into their pets' routine, they can help ensure a healthy and happy life for their beloved companions.
Consequences of Untreated Periodontal Disease
Untreated periodontal disease in dogs can lead to a range of serious health issues. Initially, the dog may experience bad breath, which is often one of the first signs of periodontal disease. However, if left unaddressed, the condition progresses rapidly, leading to more severe complications.
One of the most significant consequences of untreated periodontal disease is tooth loss. The infection and inflammation caused by the buildup of plaque and tartar can erode the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums and bone. Over time, this destruction can result in loose or missing teeth, which can impact the dog's ability to eat and maintain a healthy diet.
Moreover, the bacteria associated with periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream, a condition known as bacteremia. Once these bacteria circulate throughout the body, they can affect various organs, including the heart, liver, and kidneys. This systemic infection can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, liver damage, and kidney failure.
In addition to these internal issues, periodontal disease can also have a significant impact on the dog's overall quality of life. Chronic pain and discomfort from infected teeth and gums can cause behavioral changes, such as decreased appetite, lethargy, and irritability. Dogs with advanced periodontal disease may exhibit signs of aggression or become withdrawn due to the constant pain they experience.
Preventing periodontal disease is crucial for maintaining a dog's oral health and overall well-being. Regular dental checkups, professional cleanings, and at-home care are essential steps in preventing this common but serious condition. By addressing periodontal disease early, pet owners can help their dogs avoid the severe consequences that come with untreated infection and inflammation.
Recognizing the Signs of Dental Problems
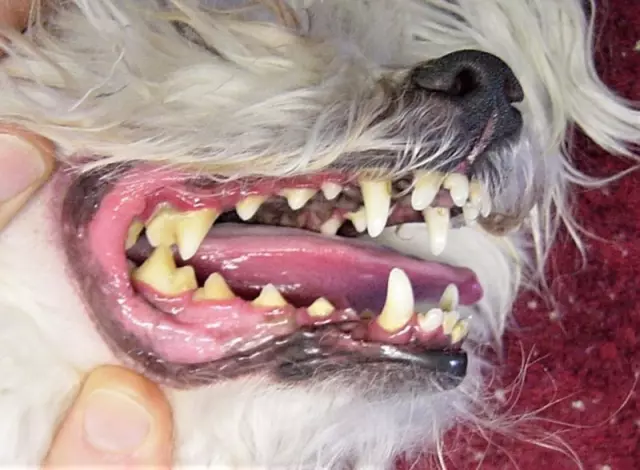
Visual Inspection: Bad Breath, Plaque and Tartar Accumulation
Visual Inspection: Bad Breath, Plaque and Tartar Accumulation
Regular visual inspection of a dog's mouth is crucial in maintaining optimal dental health. Bad breath, often characterized by an unpleasant odor, can be an early indicator of periodontal disease. While it may seem trivial, persistent bad breath warrants attention and should prompt further examination.
Plaque accumulation is another critical sign to look out for during visual inspections. Plaque appears as a thin, colorless film on the teeth's surface, particularly near the gum line. When left untreated, plaque can harden into tartar, which is more challenging to remove and can lead to significant dental issues. Tartar typically forms above the gum line and may appear yellow or brown, making it easier to spot during visual inspections.
It is essential to be vigilant about these signs as they can progress rapidly if not addressed promptly. Regular at-home dental care, including toothbrushing with veterinarian-approved toothpaste, can help prevent the buildup of plaque and tartar. Additionally, providing your dog with dental chews and toys designed to promote oral health can further mitigate the risk of periodontal disease.
However, professional dental cleanings are necessary for a comprehensive approach to dental care. During these procedures, veterinarians can remove tartar buildup effectively and assess the overall health of your dog's teeth and gums. Early detection and intervention through visual inspections and professional care are vital in preserving your dog's oral health and preventing periodontal disease.
Behavioral Changes: Difficulty Chewing, Drooling, Reluctance to Play
Behavioral Changes: Difficulty Chewing, Drooling, Reluctance to Play
One of the most evident signs that a dog may be experiencing dental issues is a change in their behavior. While it can be challenging to pinpoint exactly what is bothering your pet, observing changes in their habits and interactions can provide valuable insights into their oral health.
Difficulty Chewing: If you notice that your dog has started to chew on one side of the mouth or has become reluctant to eat hard food, it could be an indication of dental problems. Teeth affected by periodontal disease often cause discomfort and pain when chewing, leading dogs to alter their eating habits.
Drooling: Excessive drooling is another common symptom of dental issues in dogs. While some breeds are naturally prone to drooling more than others, a sudden increase in saliva production can signal oral health problems. Inflammation and infection associated with periodontal disease may cause discomfort, leading dogs to drool more frequently.
Reluctance to Play: A decrease in playful behavior is another subtle sign that your dog might be experiencing dental pain. Toys and games often involve chewing or putting pressure on the mouth, which can be uncomfortable for a dog with dental issues. If your usually energetic pet shows less interest in playing, it may be time to inspect their teeth and gums.
Regular dental care is crucial for preventing periodontal disease and maintaining overall oral health in dogs. By being vigilant about these behavioral changes, you can take prompt action to address any underlying dental issues and improve your pet's quality of life.
3. Physical Examination: Red or Swollen Gums, Loose Teeth
The physical examination of a dog's mouth is crucial in detecting signs of periodontal disease. One of the most evident indicators includes red or swollen gums, which are often accompanied by loose teeth. These symptoms are not merely cosmetic issues; they signify an underlying infection that can significantly impact a dog's overall health and well-being. Redness and swelling in the gums typically result from bacterial buildup, which forms plaque and subsequently tartar if left untreated. This inflammation can cause discomfort and pain for the dog, potentially leading to decreased appetite and changes in behavior. Loose teeth are another critical sign that should not be overlooked. They indicate advanced periodontal disease where the supporting structures of the teeth have been severely compromised. Regular veterinary check-ups and diligent home care can help detect these issues early, enabling prompt intervention and prevention of further complications.
Preventive Measures
1. Brushing Your Dog's Teeth: Frequency, Technique, Toothpaste Selection
Brushing your dog's teeth is an essential aspect of maintaining their overall health and preventing periodontal disease. Regular dental care can significantly extend the lifespan of your pet by minimizing the risk of bacterial infections that could spread to vital organs such as the heart, liver, and kidneys.
The frequency of brushing depends on various factors including the dog's age, breed, and diet. Ideally, teeth should be brushed daily to effectively remove plaque before it hardens into tartar. However, even brushing three times a week can make a substantial difference in maintaining good oral hygiene.
When it comes to technique, it is crucial to use gentle but firm pressure with the toothbrush. Begin by lifting your dog's lips to expose the teeth and gums. Gently brush the outer surfaces of the teeth in a circular motion, ensuring you cover all areas thoroughly. Pay special attention to the upper molars and canines, which are more prone to tartar buildup.
Selecting the right toothpaste is equally important. Never use human toothpaste as it contains ingredients like fluoride and xylitol that are harmful to dogs. Opt for a toothpaste specifically formulated for dogs, which comes in flavors they will find appealing such as chicken or beef. These toothpastes not only clean the teeth but also help reduce plaque buildup and freshen breath.
Incorporating regular dental care into your dog's routine is not just about maintaining a healthy mouth but also ensuring their general well-being. By being proactive, you can significantly reduce the risk of periodontal disease and its associated complications, contributing to a longer and healthier life for your beloved pet.
Dental Chew Toys and Treats: Types and Benefits
Dental Chew Toys and Treats: Types and Benefits
Maintaining optimal dental health is crucial for dogs to prevent periodontal disease. Among the various methods available, dental chew toys and treats stand out as effective and enjoyable tools for promoting canine oral hygiene. These products not only provide entertainment but also offer significant benefits in maintaining clean teeth and healthy gums.
Dental chew toys are designed with textured surfaces that help to scrape away plaque and tartar buildup as dogs chew. The act of chewing itself stimulates saliva production, which naturally contains enzymes that break down bacteria and promote oral health. Toys made from durable materials like rubber or nylon are particularly effective, as they can withstand the force of a dog's jaws and provide long-lasting benefits.
Similarly, dental treats are formulated to combat plaque and tartar accumulation. These treats often contain specific ingredients such as enzymes or abrasives that mechanically clean teeth and inhibit bacterial growth. Some treats even have a unique shape or design that encourages thorough chewing, ensuring maximum contact with the dog's teeth and gums.
The benefits of incorporating dental chew toys and treats into a dog's routine are multifaceted. Regular use can help reduce the risk of periodontal disease by minimizing plaque and tartar buildup. This, in turn, reduces the likelihood of bad breath, which is often a symptom of poor oral health. Furthermore, maintaining good dental hygiene through these methods can contribute to overall systemic health, as bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream and affect other organs.
When selecting dental chew toys and treats for your dog, it is essential to consider factors such as size, age, and breed. Opting for products that are specifically designed for your dog's needs will ensure they receive the maximum benefits. Additionally, always supervise your dog while they are using these products to prevent any potential choking hazards or accidents.
In conclusion, dental chew toys and treats offer a practical and enjoyable way to support canine oral health. By incorporating these products into your dog's routine, you can significantly contribute to the prevention of periodontal disease and promote overall well-being.
3. Professional Dental Cleanings: Importance and Frequency
Professional dental cleanings play a crucial role in maintaining the oral health of dogs and preventing periodontal disease. Regular cleanings help remove plaque and tartar buildup, which can lead to gingivitis and other serious dental issues if left untreated. The frequency of these cleanings may vary depending on the dog's breed, age, and overall oral health condition. It is recommended that dogs undergo professional dental cleanings at least once a year to ensure optimal oral hygiene and prevent the progression of periodontal disease. Additionally, regular at-home dental care, such as brushing teeth and providing dental chews or toys, can complement professional cleanings in maintaining good oral health for dogs.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
1. Scaling and polishing: removing plaque and tartar
Scaling and polishing are crucial procedures in maintaining optimal oral health for dogs. This process involves the removal of plaque and tartar, which are primary contributors to periodontal disease. Plaque is a thin film of bacteria that accumulates on teeth, while tartar is a hardened form of plaque that adheres firmly to tooth surfaces. Both substances can lead to inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) and, if left untreated, progress to more severe issues such as periodontitis, which affects not only the mouth but also overall health.
During a scaling and polishing session, veterinary professionals use specialized tools to meticulously scrape away plaque and tartar from both above and below the gum line. This procedure helps to restore the teeth's natural smoothness and prevents further buildup of harmful substances. It is essential to note that while at-home dental care routines, such as brushing and using dental chews, can help maintain oral hygiene, professional scaling and polishing are necessary for a thorough cleanse and to address areas that pet owners may not be able to reach effectively.
Regular scaling and polishing sessions, typically recommended annually or as advised by a veterinarian, play a significant role in preventing the onset of periodontal disease and maintaining overall canine health. By keeping teeth free from plaque and tartar, dogs are less likely to experience pain, bad breath, and other complications associated with poor oral hygiene.
Extraction: Removal of Severely Damaged Teeth
Extraction is a crucial procedure in dental care for dogs, specifically when dealing with severely damaged teeth. The removal of such teeth is essential to prevent the spread of infection and maintain overall oral health. When a tooth is severely damaged or infected, it can no longer serve its intended purpose effectively. Moreover, the damage can extend beyond the tooth itself, affecting surrounding tissues and potentially causing systemic issues if left untreated.
The extraction process involves careful removal of the affected tooth under general anesthesia to ensure the dog's comfort and safety. This procedure is typically performed by a veterinary dentist or a trained veterinarian with expertise in dental surgery. After the extraction, proper aftercare is essential to facilitate healing and prevent complications such as infection or dry socket.
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are vital for maintaining good oral hygiene in dogs and preventing periodontal disease. Early detection of dental issues through routine examinations can help avoid the need for extractions by addressing problems before they become severe. Additionally, regular at-home dental care, including brushing and providing appropriate chew toys, can significantly contribute to preserving a dog's dental health.
In summary, extraction is a necessary aspect of dental care for dogs with severely damaged teeth. It helps prevent the spread of infection and promotes overall oral health. Regular check-ups and diligent at-home care are key to maintaining good dental hygiene and minimizing the risk of periodontal disease in dogs.
Medications: Antibiotics, Painkillers
Medications, such as antibiotics and painkillers, play a crucial role in managing dental care for dogs, particularly when preventing periodontal disease. Antibiotics are often prescribed to combat bacterial infections that can occur beneath the gum line or within tooth pockets. These medications work by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria, thereby reducing inflammation and preventing further damage to the teeth and surrounding tissues. Painkillers, on the other hand, are essential for alleviating discomfort associated with dental procedures or advanced stages of periodontal disease. By administering these medications appropriately, pet owners can significantly improve their dogs' oral health and overall well-being.